1930 E. Rosemeade Pkwy #103 Carrollton, TX 75007
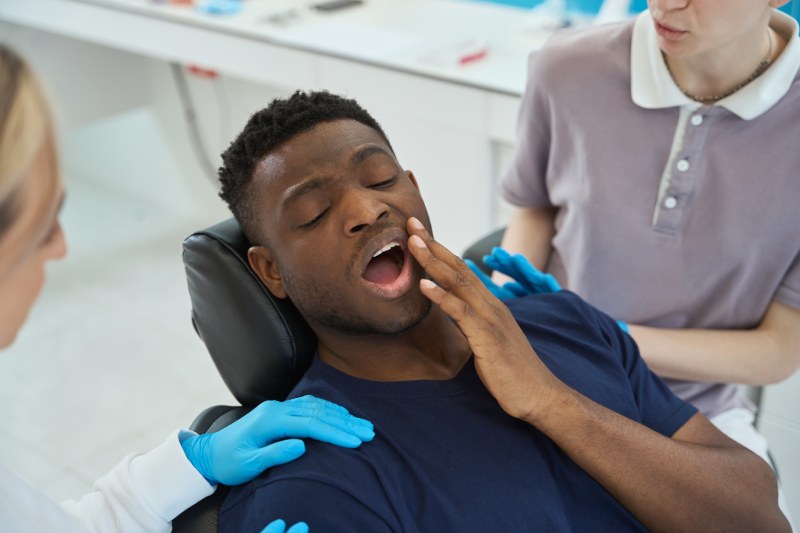
A dental abscess is a common yet serious dental condition that arises when a bacterial infection leads to a pocket of pus within the teeth, gums, or surrounding bone.
Though it may begin as a minor toothache or gum swelling, if left untreated, it can evolve into a significant health issue with the potential to affect the entire body.
Understanding what a dental abscess looks like, its causes, how it is treated, and when it becomes a dental emergency can help in the timely management and prevention of further complications.
What Does a Dental Abscess Look Like?
A dental abscess often presents as a swollen, red, and tender area in the mouth. It can occur in different parts of the tooth or gum:
- A periapical abscess is found right at the tip of a tooth’s root.
- Periodontal abscess: Occurs in the gum tissue next to a tooth root.
- Gingival abscess: Forms in the gum tissue without affecting the tooth or periodontal ligament.
You might notice a bump or pimple-like swelling on the gums, sometimes accompanied by pus drainage. The area around the abscess can appear inflamed and may bleed when touched. In advanced stages, facial swelling, fever, or a foul taste in the mouth may also develop.
What Causes a Dental Abscess?
The primary cause of a dental abscess is a bacterial infection, which can develop from several dental issues:
- Tooth decay that goes untreated can cause cavities to reach the inner pulp, which may result in an infection.
- If you have cracked or broken teeth, it’s important to know that this damage can create an opening for bacteria to invade the tooth pulp.
- Gum disease (periodontitis) – Deep pockets and receding gums offer easy access for bacteria.
- Poor oral hygiene – Inadequate brushing and flossing promote bacterial buildup.
- Previous dental procedures – Incomplete treatments or failed restorations can allow bacteria to linger.
Once bacteria reach the pulp (the soft inner part of the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels), they multiply, leading to inflammation, tissue death, and pus formation. The body’s immune response attempts to fight off the infection, but without proper treatment, the abscess can worsen and spread.
What Antibiotics Treat Dental Abscesses?
While antibiotics are not always the first line of treatment, they may be prescribed in certain cases, particularly if the infection has spread or if the patient exhibits systemic symptoms such as fever or swelling.
Common antibiotics used to treat dental abscesses include:
- Amoxicillin – Often the first choice unless the patient has an allergy.
- Clindamycin – Prescribed if the patient is allergic to penicillin-based drugs.
- Metronidazole – Sometimes used in combination with amoxicillin for more complex infections.
- Cephalexin – Another alternative for penicillin-sensitive individuals.
Keep in mind that antibiotics can’t fully take care of a dental abscess on their own. They might help keep the infection in check temporarily, but you’ll need a dentist to actually eliminate the source of the infection.
When Is a Dental Abscess an Emergency?
While many dental abscesses begin as mild to moderate discomfort, certain signs indicate that immediate medical or dental attention is needed:
- Rapid facial swelling
- High fever and chills
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Severe, persistent toothache
- Swelling extending to the eye or neck
These symptoms may suggest that the infection is spreading beyond the oral cavity, potentially affecting the jaw, throat, or bloodstream. In such cases, the abscess becomes a medical emergency and may require urgent surgical drainage or hospitalization.
Are Dental Abscesses Painful?
Yes, dental abscesses are typically very painful. The pressure caused by the accumulation of pus inside the confined space of a tooth or gum leads to intense throbbing pain.
The pain can be constant or intermittent, and it often worsens when lying down, chewing, or touching the affected area. In some cases, the pain may radiate to the ear, jaw, or neck on the same side as the infected tooth.
Pain is your body’s way of signaling that something is wrong. Ignoring it or relying solely on over-the-counter pain relievers may delay essential treatment and increase the risk of serious complications.
How to Drain a Dental Abscess (Professional Treatment)
Draining a dental abscess is a professional procedure that a dentist must perform. The goal is to eliminate the source of the infection and relieve pressure. The exact approach you take will vary based on the kind and seriousness of the abscess:
Incision and Drainage
A dentist makes a small cut in the abscess to release the pus. The area is then cleaned and, if necessary, a small rubber drain is inserted to allow further drainage.
Root Canal Treatment
For a periapical abscess, the best course of action is to perform a root canal treatment. This process takes out the infected pulp, cleans the canal, and seals the tooth up tight. It effectively gets rid of the infection while ensuring the natural tooth remains.
Periodontal Therapy
In the case of a periodontal abscess, deep cleaning techniques such as scaling and root planing are employed. Severe cases may require flap surgery or tissue removal.
Tooth Extraction
If the tooth is severely damaged and cannot be saved, extraction may be the only viable option. After removal, the area is cleaned and allowed to heal.
After treatment, dentists typically prescribe antibiotics to ensure all remaining bacteria are eliminated, along with pain management strategies to help recovery.
Conclusion: The Importance of Timely Professional Care
A dental abscess should never be ignored. While it may start as a mild toothache or swelling, it can progress rapidly into a severe infection that affects more than just your oral health. Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms early, and seeking professional dental care are key to preventing complications and preserving the health of your teeth and gums.
If you’re in Carrollton and experiencing signs of a dental abscess—such as persistent pain, swelling, or sensitivity—consulting a professional Carrollton dentist is essential. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment, whether through drainage, root canal therapy, or periodontal care, can prevent the spread of infection and ensure effective recovery.
Getting ahead of dental issues not only helps you feel better now but also ensures your long-term dental and overall health stays in great shape.

